Beyond the Headlines: Understanding the Ongoing Relevance of the North Caucasus
Kavkaz Files ISSN 2975-0474 Volume 17 Issue 2
Author: Giuliano Bifolchi
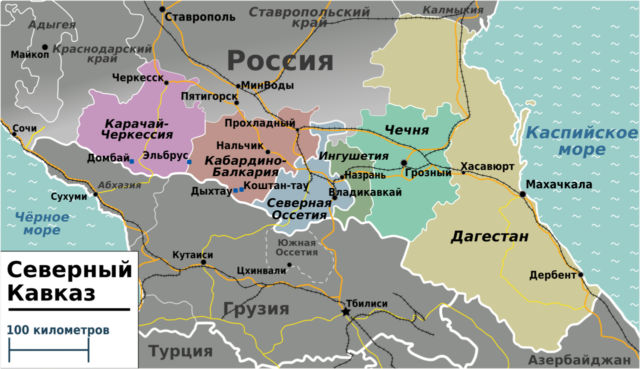
The North Caucasus holds a crucial position on the Eurasian geopolitical chessboard. Serving as a natural bridge between Europe and Asia, and a barrier/frontier between the Muslim and Christian world, the region’s significance cannot be overlooked. This report highlights the reasons the North Caucasus remains important and necessitates ongoing monitoring.
The Role of the North Caucasus in Kremlin’s Domestic and Foreign Policy
The North Caucasus plays a fundamental role in the Kremlin’s domestic and foreign policy objectives. With a significant Muslim population, Moscow has utilised the region to establish links with the Arab-Muslim world. Moreover, stabilising and controlling the North Caucasus enables Moscow to extend its influence in the South Caucasus, Black Sea, Caspian Sea, Middle East, and Central Asia.
During the 1990s and the early 21st century, the North Caucasus attracted substantial interest from international media and scholars because of the Kremlin’s struggle against local ethnonationalist movements and entanglement in the Chechen conflict, followed by the fight against groups like Imarat Kavkaz (Caucasus Emirate).
Recently, apart from Chechnya’s role in supporting Russia during the Ukraine conflict, the North Caucasus has seen a decline in interest because of reduced violent attacks and victims.
As we several times reported at SpecialEurasia, considering the Ukraine conflict, the Kremlin has intensified its efforts and investments in the North Caucasus. The aim is to transform the region into a regional logistic hub, connecting it with Iran, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa.
Events such as the first Caucasian Investment Exhibition and the forum “Severnyj Kavkaz v menjajushhemsja mire” (The North Caucasus in a Changing World) underscore the Kremlin’s strategy, leveraging the North Caucasus to counter Western sanctions and establish ties with emerging markets in the Arab-Muslim world.
Dagestan and Chechnya stand out as the most prominent republics in the North Caucasus. The Kremlin has started a pilot project on Islamic Banking in these two republics (alongside Tatarstan and Bashkortostan), aiming to attract investors from the Arab-Muslim world, particularly the United Arab Emirates and Qatar, and harness Islamic financial products.
Chechnya’s diplomacy in the Middle East and Gulf Arab monarchies contributes to its influential role in foreign politics. Dagestan, with its strategic position and the development of the Makhachkala Sea Trade Port, is poised to better connect Russia with Iran and Central Asia and support the International North-South Transport Corridor and enhance Russian trade with these markets.
While the region is not immune to terrorist threats and jihadist propaganda, the Kremlin recognises the potential impact of weakening support for local forces and authorities on regional stability. By attracting investments in the North Caucasus, the Kremlin seeks alternative solutions beyond military force and counter-terrorism operations.
Risk Assessment Scenarios
The North Caucasus keeps its strategic importance as a vital link between Europe and Asia, and as a frontier between the Muslim and Christian world. The Kremlin’s focus on the region, coupled with past and current developments, highlights the need for continuous monitoring.
Understanding the region’s significance and dynamics will enable policymakers to navigate the challenges and opportunities associated with the North Caucasus effectively.
At SpecialEurasia, we evaluated the potential scenarios concerning the North Caucasus:
Scenario 1: Regional Stability and Economic Growth
In this scenario, the Kremlin’s increased efforts and investments in the North Caucasus pay off, resulting in improved stability and economic growth in the region. Counter-terrorism measures, coupled with socio-economic development initiatives, effectively curb terrorist threats and jihadist propaganda. The North Caucasus becomes a flourishing hub for trade and investment, contributing to the overall stability and prosperity of the region.
Scenario 2: Lingering Ethnic Tensions and Unrest
Despite the Kremlin’s efforts, ethnic tensions and unrest persist in the North Caucasus thanks also to foreign interferences provided by the West, Turkey and some Arab countries. Local ethnonationalist movements gain momentum, challenging Moscow’s control over the region. The resurgence of violence and radicalisation pose significant security threats, requiring intensified counter-terrorism operations. The region remains a source of concern, both domestically and internationally, as instability continues to hinder socio-economic progress.
Scenario 3: Increased Regional Autonomy
In this scenario, demands for greater regional autonomy gain traction in the North Caucasus. Local authorities push for decentralisation, seeking more control over governance and resources. Moscow faces challenges in balancing central authority and regional aspirations. Negotiations and political compromises become necessary to address grievances and maintain stability, potentially reshaping the region’s political landscape.
Scenario 4: External Influence and Power Struggles
External actors, including neighbouring countries and international powers, recognise the strategic importance of the North Caucasus and actively seek to exert influence. Competing interests and power struggles intensify, leading to a complex geopolitical environment. The region becomes a battleground for proxy conflicts and competition for resources, further complicating efforts to achieve stability and socio-economic progress.
Scenario 5: Gradual Integration and Collaboration
In a more optimistic scenario, the North Caucasus gradually integrates into the broader Eurasian region, fostering collaboration and cooperation. The region becomes a key player in regional initiatives, such as the International North-South Transport Corridor, facilitating trade and connectivity. Through diplomatic engagement and inclusive policies, Moscow successfully addresses the concerns of local populations, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity within the Russian Federation. This leads to increased stability and a positive trajectory for the region’s development.
Do you like SpecialEurasia reports and analyses? Has our groundbreaking research empowered you or your team? Now is your chance to be a part of our mission! Join us in advancing independent reporting and unlocking the secrets of Eurasia’s complex geopolitical landscape. Whether through a one-time contribution or a monthly/yearly donation, your support will fuel our relentless pursuit of knowledge and understanding. Together, let’s pave the way for a brighter future. DONATE NOW and secure your place in shaping the geopolitical narrative.
